1. Sql 과 Dao의 분리
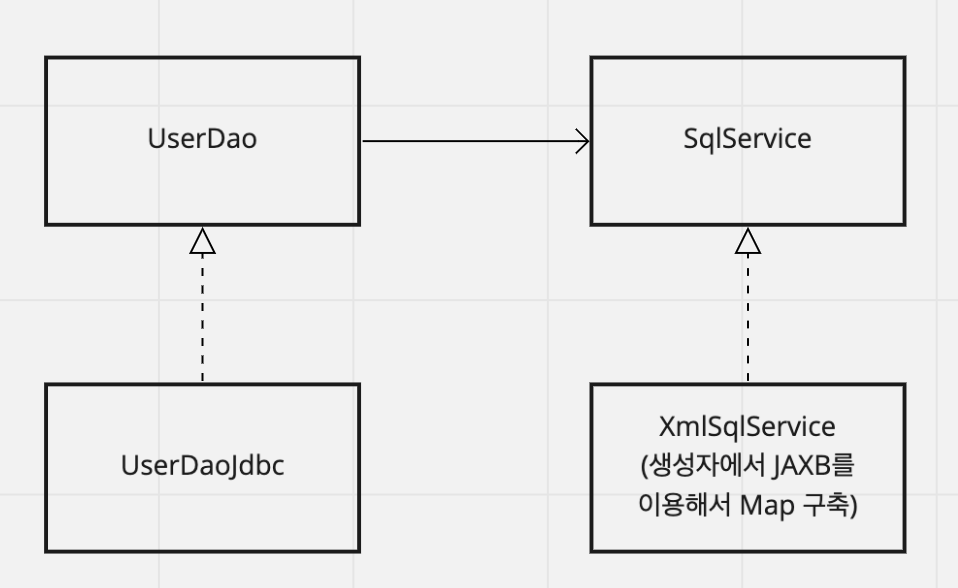
현재의 구조는 Dao 내부에서 Sql을 정의하여 사용하도록 되어있다.
- 토비의 스프링에서는 이를 JAXB api를 사용하여 xml에 따로 sql을 관리하도록 하여 저장하도록 구현한다.
- 변경된 현재구조는 아래와 같다.
public class XmlSqlService implements SqlService {
private Map<String, String> sqlMap = new HashMap<>();
public XmlSqlService() {
String contextPath = Sqlmap.class.getPackage().getName();
try {
JAXBContext context = JAXBContext.newInstance(contextPath);
Unmarshaller unmarshaller = context.createUnmarshaller();
InputStream is = UserDao.class.getResourceAsStream("/sqlmap.xml");
Sqlmap sqlmap = (Sqlmap) unmarshaller.unmarshal(is);
for(SqlType sqlType : sqlmap.getSql()) {
sqlMap.put(sqlType.getKey(), sqlType.getValue());
}
} catch (JAXBException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}생성자 내에서 예외가 발생할 수 있는 초기화작업은 좋지않다.
- 생성자 생성중 발생 예외는 다루기 힘들다.
- 상속하기 불편하다.
- 함수를 하나 만들어서 수행하도록 변경한다.
생성자에서 파일을 읽어오는 구조에서
- 파일을 읽어들이는 함수를 하나 구현한 뒤
- @PostConstruct(빈 오브젝트를 생성하고, DI 가 끝난 뒤에 메소드를 자동 수행) 빈 후처리기 어노테이션을 이용해서 등록한다.
public class XmlSqlService implements SqlService {
private Map<String, String> sqlMap = new HashMap<>();
private String sqlmapFile;
public void setSqlmapFile(String sqlmapFile) {
this.sqlmapFile = sqlmapFile;
}
@PostConstruct
public void loadSql() {
String contextPath = Sqlmap.class.getPackage().getName();
try {
JAXBContext context = JAXBContext.newInstance(contextPath);
Unmarshaller unmarshaller = context.createUnmarshaller();
InputStream is = UserDao.class.getResourceAsStream(sqlmapFile);
Sqlmap sqlmap = (Sqlmap) unmarshaller.unmarshal(is);
for(SqlType sqlType : sqlmap.getSql()) {
sqlMap.put(sqlType.getKey(), sqlType.getValue());
}
} catch (JAXBException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}현재 XmlSqlService의 구조를 보면
- SQL 파일을 읽어들이는 기능
- SQL 문을 등록하는 기능
- SQL 문을 조회하는 기능
이를 인터페이스로 분리하여
- SQL 파일을 읽어들이는 기능
- SQL 파일을 등록 / 조회하는 기능으로 나눠서 변경해보자
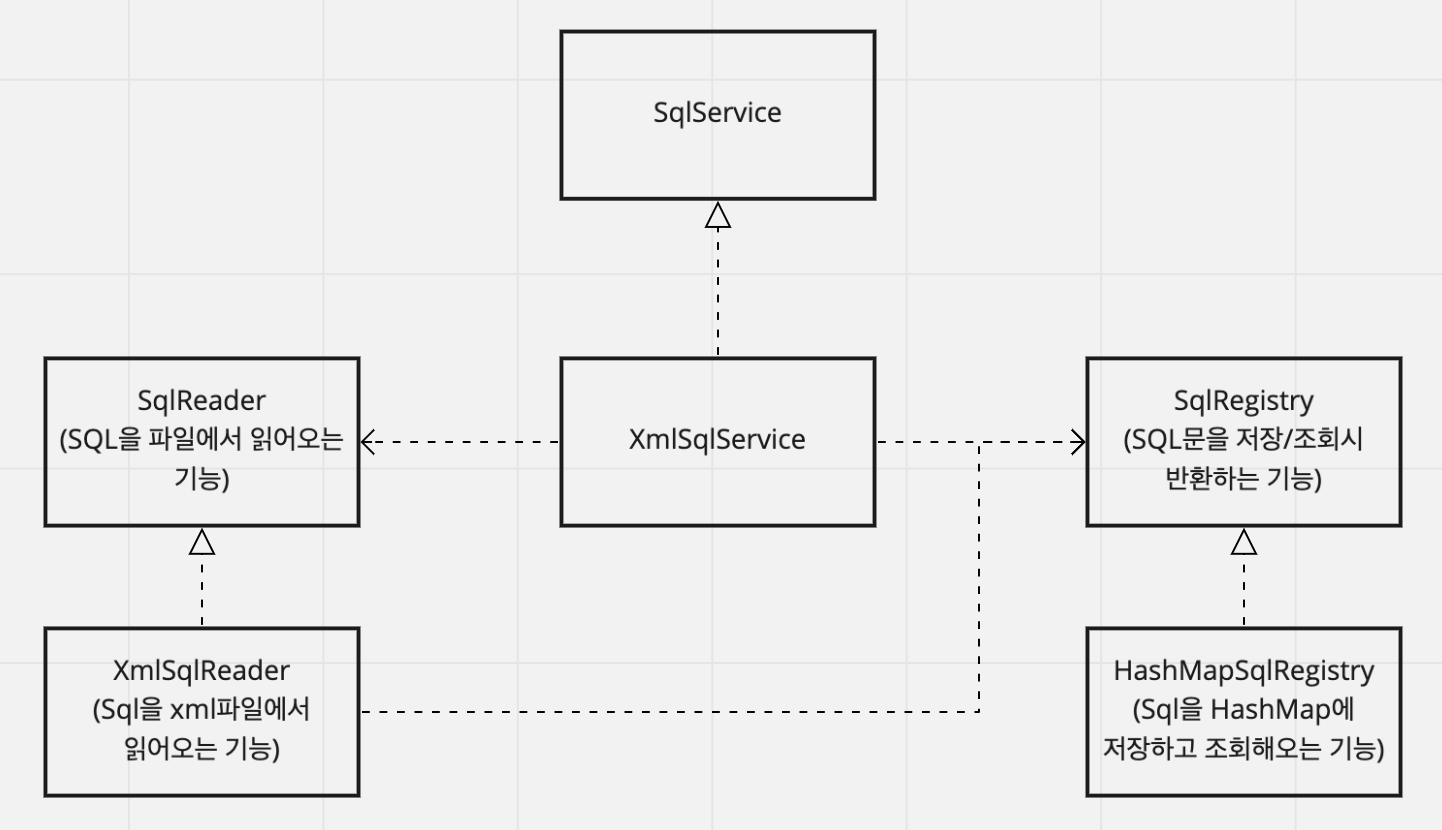
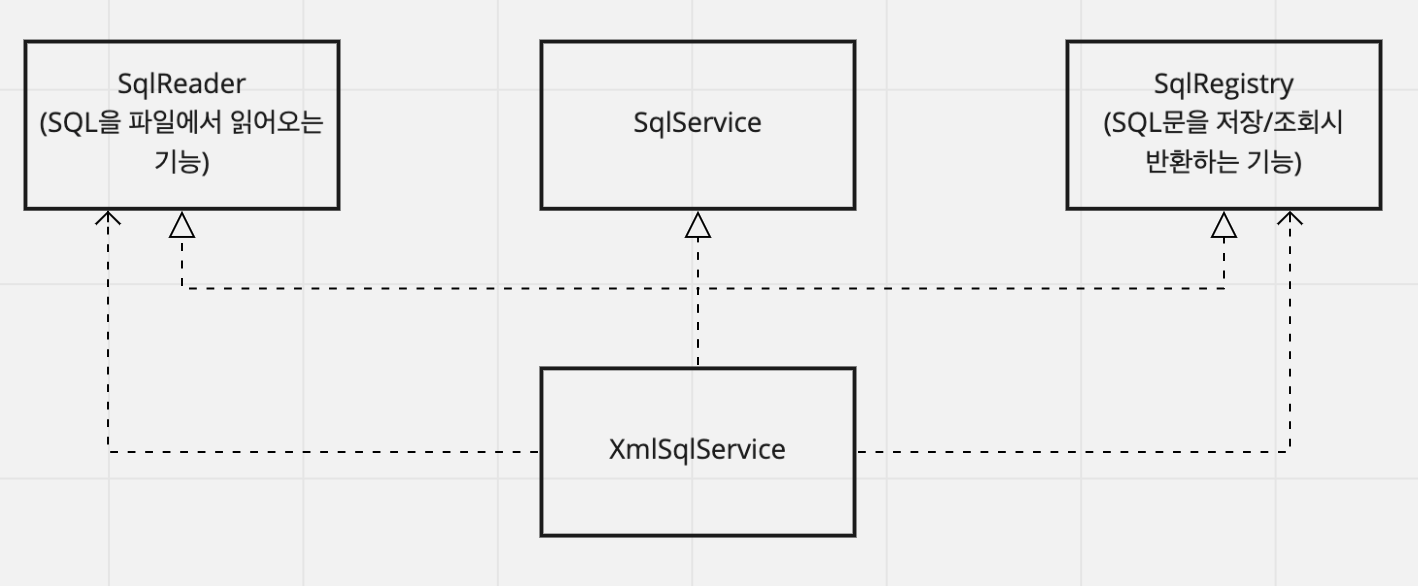
해당 코드는 현재 하나의 관심사 (Xml을 읽어서 저장하고 반환하는 기능) 을 갖고있기 때문에 인터페이스 다중상속을 이용하여 아래와같이 구조를 잡을 수 있다.
public class XmlSqlService implements SqlService, SqlRegistry, SqlReader {
private SqlReader sqlReader;
private SqlRegistry sqlRegistry;
private String sqlmapFile;
private Map<String, String> sqlMap = new HashMap<>();
public void setSqlReader(SqlReader sqlReader) {
this.sqlReader = sqlReader;
}
public void setSqlRegistry(SqlRegistry sqlRegistry) {
this.sqlRegistry = sqlRegistry;
}
@PostConstruct
public void loadSql() {
sqlReader.read(sqlRegistry);
}
/**
* SqlService Implementation
*/
@Override
public String getSql(String key) throws SqlRetrievalFailureException {
try {
return sqlRegistry.findSql(key);
} catch(SqlNotFoundException e) {
throw new SqlRetrievalFailureException(e);
}
}
/**
* SqlRegistry Implementation
*/
@Override
public void registerSql(String key, String sql) {
sqlMap.put(key, sql);
}
@Override
public String findSql(String key) throws SqlNotFoundException {
String sql = sqlMap.get(key);
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(sql)) {
throw new SqlNotFoundException(key + "를 이용해서 SQL을 찾을 수 없습니다.");
}
return sql;
}
/**
* SqlReader Implementation
*/
@Override
public void read(SqlRegistry sqlRegistry) {
String contextPath = Sqlmap.class.getPackage().getName();
try {
JAXBContext context = JAXBContext.newInstance(contextPath);
Unmarshaller unmarshaller = context.createUnmarshaller();
InputStream is = UserDao.class.getResourceAsStream(sqlmapFile);
Sqlmap sqlmap = (Sqlmap) unmarshaller.unmarshal(is);
for(SqlType sqlType : sqlmap.getSql()) {
registerSql(sqlType.getKey(), sqlType.getValue());
}
} catch (JAXBException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}위의 구조로 성격이 다른 코드들을 인터페이스를 통해 분리해냈다.
- 빈 등록을 하려면 어떻게해야할까?
- 자신이 구현했으면서, 자신을 빈으로 등록하는 경우에는 아래와같이 자기자신을 참조하도록 설정한다.
@Bean
public SqlService sqlService() {
XmlSqlService sqlProvider = new XmlSqlService();
sqlProvider.setSqlmapFile("/sqlmap.xml");
sqlProvider.setSqlReader(sqlProvider);
sqlProvider.setSqlRegistry(sqlProvider);
return sqlProvider;
}2. 서비스 추상화 적용
두가지 기능을 더 추상화한다.
- JAXB 외에도 XML을 자바 오브젝트로 매핑할수 있기에, 이를 추상화한다.
- OXM (Object-XML Mapping)
- 클래스패스 안에서만 XML을 읽어오는 기능을 추상화한다.
OXM 추상화
- 스프링에서 제공하는 Unmarshaller 인터페이스를 사용해서 추상화 할 수 있다.
- 과정은 토비의스프링에서..
리소스 추상화
- 스프링 Resource 인터페이스를 사용한다.
- ApplicationContext가 ResourceLoader를 상속하고 있기에
- ResourceLoader 을 사용하여 Prefix 기반으로 오브젝트를 반환하는 기능을 사용한다.
package org.springframework.core.io;
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {
boolean exists();
default boolean isReadable() {
return exists();
}
default boolean isOpen() {
return false;
}
default boolean isFile() {
return false;
}
URL getURL() throws IOException;
URI getURI() throws IOException;
File getFile() throws IOException;
default ReadableByteChannel readableChannel() throws IOException {
return Channels.newChannel(getInputStream());
}
long contentLength() throws IOException;
long lastModified() throws IOException;
Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException;
@Nullable
String getFilename();
String getDescription();
}
| prefix | desc |
| file: | C:/temp 폴더 기준 |
| classpath: | 클래스패스 루트 기준 |
| 없음 | ResourceLoader 구현에 따라 달라진다. |
| http: | Http 프로토콜을 사용해서 웹상의 리소스를 가져온다. / ftp: 도 가능하다. |
3. 인터페이스 상속
현재 구조에서 SqlRegistry 에 업데이트 하는 기능이 추가된다면?
- 지금까지 추상화를 이용한 분리를 잘 해왔기에 간단하게 인터페이스 상속을 통해 다른 클래스들은 변경하지않고 추가할 수 있다.
public interface UpdatableSqlRegistry extends SqlRegistry {
void updateSql(String key, String sql) throws SqlUpdateFailureException;
void updateSql(Map<String, String> sqlMap) throws SqlUpdateFailureException;
}4. 스프링 3.1의 DI
두가지 변화
- 어노테이션 메타정보 활용
- Reflection API 를 이용하여 자바클래스 / 인터페이스 / 필드 / 메소드 등 메타정보를 살펴보기 시작
- 자바 5에서 어노테이션이 나타난 이후, Reflection API 를 이용하여 어노테이션의 메타정보를 조회하고, 설정된 값을 사용
- 기존에는 xml을 이용해서 했으나
- ex) <bean id="userService", class="www.sjlee.kr.UserService.class"/ >
- 어노테이션을 통해서 간단하게
- 클래스에 대한 메타정보
- 클래스의 패키지, 이름, 접근제한자, 메소드 등을 알 수 있다.
<tx:annotation-driven /> 은 아래와 같은 클래스들을 빈으로 등록해준다.
- InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
- AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource
- TransactionInterceptor
- BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor
해당 <tx:annotation-driven/> 은 @EnableTransactionManagement 로 대체하여 위의 빈들을 등록하게한다.
- XML 에서 자주 사용되는 설정들을 @Enable+... 으로 스프링은 해결하도록 해놓았다.
@Component 는
- @ComponentScan 을 통해 스캔할 수 있도록 지정해줘야 한다.
@Import
- 빈을 등록하는 Configuration 클래스가 2개인 경우에
- 1. 전체를관리하는 AppContext (메인 설정정보)
- 2. sql 연결쪽을 관리하는 SqlServiceContext (보조 설정정보)
@Configuration
@Import(SqlServiceContext.class)
public class AppContext {
}
@Profile
- 특정 프로파일에만 적용돼야 하는 빈 설정을 갖고있는다.
@ActiveProfiles
- 해당 테스트를 해당 프로파일로 실행하도록 한다.
@PropertySource
- 등록한 리소스로부터 프로퍼티의 값을 가져올 수 있다.
- @Bean 에서 등록할 때에는 npe 발생 ..ㅠ
- 아래와 같이 사용
# database.properties
db.driverClass=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
db.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/tobyspring?serverTimezone=UTC&characterEncoding=UTF-8
db.username=root
db.password=123123@Getter
@Component
@PropertySource("classpath:database.properties")
public class DatabaseProperty {
@Value("${db.driverClass}")
String driverClass;
@Value("${db.url}")
String url;
@Value("${db.username}")
String username;
@Value("${db.password}")
String password;
}- @Value(${}) 방식을 placeholder 방식이라고 하며, 이를 사용하기 위해서는
- PropertySourcePlaceHolderConfigurer 을 등록해줘야 한다. (Springboot는 알아서 등록이 되는 것 같다.)
@EnableTransactionManagement 어노테이션
- @Import(TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector.class)
- TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector 클래스의 설정정보를 임포트하겠다는 뜻이다.
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector.class)
public @interface EnableTransactionManagement {
..
}'책 정리 > 토비의 스프링' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 8. 스프링이란 무엇인가 (0) | 2021.02.20 |
|---|---|
| 6.2. 스프링 AOP (0) | 2021.02.10 |
| 6.1. AOP (0) | 2021.02.02 |
| 5. 서비스 추상화 (0) | 2021.02.01 |
| 4. 예외 (0) | 2021.01.30 |

